Flavonoids
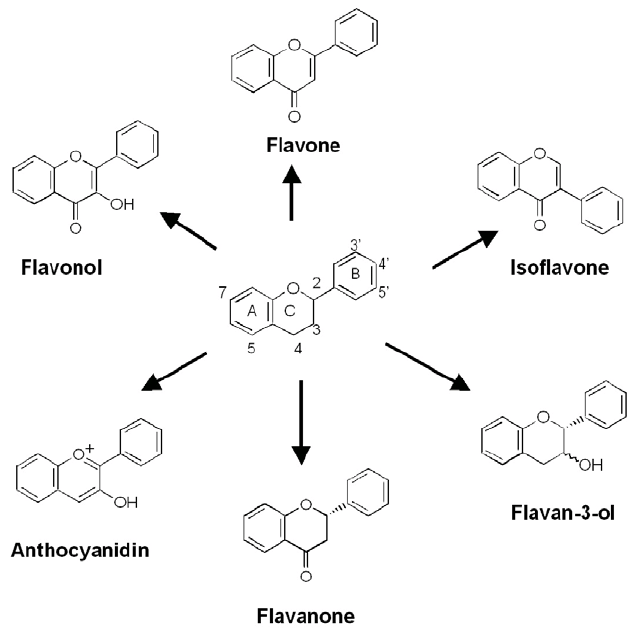
Flavonoids, a ubiquitous group of plant secondary metabolites with a 15-carbon structure (two phenyl rings and a heterocyclic ring; C6-C3-C6) are an indispensable component of traditional medicines, current nutraceuticals, and functional foods. They are the most abundant polyphenols in the human diet.
Dietary flavonoids are found in tea, berry fruit, citrus and other fruit and legumes. There are more than 6,000 identified flavonoids which have been classified into six major subgroups, outlined in the table below.
| Flavonoid Subgroup | Specific Flavonoids | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Flavonols | Quercetin, kaempferol myricetin, isorhamnetin | Onions, apples, leafy vegetables, berries |
| Flavones | Luteolin, apigenin | Parsley, hot peppers, celery, artichokes, spices |
| Flavanones | Hesperetin, naringenin, eriodictyol | Citrus fruits and citrus juices |
| Flavan-3-ols | Catechins, epigallocatechins, theaflavins | Tea, chocolate, tree fruits, grape seed |
| Anthocyanidins | Cyanidin, delphinidin, malvidin, pelargonidin, peonidin, petunidin | Most berries, cowpeas |
| Isoflavones | Daidzein, genistein, glycitein | Soybeans, soyfoods |